There are a wide range of galvanization methods,
but they are generally divided between electroplating,
which uses electricity during the course of processing, and electroless plating,
which does not use electricity.
The hot-dip galvanized coating conducted at Marco Galvanizing Co., Ltd.
falls into the latter category,
as our company’s main objective is to protect industrial products from rusting.
Objects that you see on a daily basis such as guardrails, street poles,
and staircases of apartment buildings are all pretreated
with hot-dip galvanized coating and further coated with paint or concrete.
The strong point of hot-dip galvanized coating is that it is very easy to handle.
With super durability, hot-dip galvanized steel can prevent rusting for over 50 years
in urban areas and over 10 years in coastal areas.
Although galvanized steel is used for various purposes in places all over,
it is often obscured from plain view… That is why we refer to it as
the “muscle hidden under the greenery”.

Features and Advantages of Hot-dip Galvanized Coating
Differences between coating and hot-dip galvanized coating
Coating is often compared to hot-dip galvanized coating.
The advantages of coating are that there are a wide range of colors and types to choose from, and it looks pretty from the outside.
However, there is a significant difference in the anticorrosive performances between coating and hot-dip galvanized coating.
With coating, the process must be repeated every 4-5 years or else the anticorrosive performance will not last.
If additional months or years pass by, the colors will begin to fade and the overall appearance will change.
Coating is easily affected by scratches and scuffs, and when the coated surface is exposed to such scratching, rust will develop and eat away at the base material (steel under the coating).
Protective coating agents and sacrificial protection agents are two main features of hot-dip galvanized coating.
-
- Protective coating agents are resistant to rust
-
The oxide layer of the zinc that develops on the surface of the galvanized coating contains a stable disposition that prevents oxygen or water from entering, thus preventing rusting. This feature can be seen in the general atmosphere, under water, soil, and concrete.
-
- Sacrificial protection agents are resistant to scratches and scuffs
-
The galvanized coating on the surface of steel products act as a protective coating that protects them from corrosive environments. As a result, even if scratches or scuffs occur and the iron of the foundation is exposed, the zinc surrounding the scratches and scuffs are sacrificed due to the electrochemical action (galvanic action), and will melt before the iron, preventing it from corroding.
5 Advantages of Hot-Dip Galvanized Coating
- 1. Superb adhesiveness
- Unlike other types of coating, hot-dip galvanized coating sticks due to the alloying reaction between iron substrates and zinc, preventing it from separating except in the case of excessive shock or friction.
- 2. Resistant to peeling
- An alloy layer between iron and zinc is formed on the hot-dip galvanized coating’s plating film, providing a strong adhesion with iron substrates. When handled under normal conditions, the coating will not peel off due to shock or friction.
- 3. Highly economical
- Hot-dip galvanized coating offers long-term anti-corrosion effects, (may be regional differences due to different environments) so supplementary anti-corrosion methods are hardly necessary. In theory, electrochemical action protects the surface zinc plating layer of steel products from rusting until it is completely consumed, so if your objective is long-term corrosion protection, it is the most economical method compared with other rust preventative methods.
- 4. Galvanizing is possible with different sizes
- Galvanizing is possible with different sizes. Any steel products that can be dipped into the plating tank can be galvanized. Our kettle can support a wide range of sizes, and it is possible to galvanize large-scale products of up to 11 meters.
- 5. Galvanizing is possible with any shape
- An advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that it enables you to galvanize areas that can’t usually be reached by hand. For example, molten zinc can enter and leave objects such as long thin tubes or hollow bodies.
Classification
Coatings are classified into seven classes according to coating thickness. The symbols of classification shall be as given in Table 1.
Please scroll
Table 1 Symbols of classification
| Symbols of classification | Example of application a) (informative) |
|---|---|
| HDZT 35 | Substrate of 5 mm or less in thickness, bolts and nuts of 12 mm and over in diameter, washers of over 2.3 mm in thickness, etc. for which lumpiness and run of zinc is removed by centrifugation or thin coating thickness is required for functional purposes |
| HDZT 42 | Substrate of over 5 mm in thickness for which lumpiness and run of zinc is removed by centrifugation or thin coating thickness is required for functional purposes |
| HDZT 49 | Substrate of 1 mm or over in thickness, bolts and nuts of 12 mm and over in diameter, washers of over 2.3 mm in thickness |
| HDZT 56 | Substrate of 2 mm or over in thickness | HDZT 63 | Substrate of 3 mm or over in thickness |
| HDZT 70 | Substrate of 5 mm or over in thickness |
| HDZT 77 | Substrate of 6 mm or over in thickness |
| Note a) The thicknesses and diameters given in the column of example of application are nominal dimensions. | |
JIS-H-9124 Hot-dip galvanizing working standard
JIS-H-0401 Hot-dip galvanizing test method
- There are also the following hot-dip galvanizing product standards.
-
- ・JIS H 2107 Zinc ingots
- ・JIS G 3302 Hot-dip Zinc-coated steel sheet and strip
- ・JIS G 3442 Galvanized steel pipes for ordinary piping
- ・JIS G 3532 Low carbon steel wires
- ・JIS G 3537 Zinc-coated steel wire strands
Hot-dip galvanizing process
Here we will introduce our company’s hot-dip galvanizing process

Structure Process
In order to advance the steel materials to the pretreatment process, they are assembled into optimal shapes depending on the required shape, number of units, and standards using various types of jigs.


Pretreatment Process
- Degreasing Tank
- The steel materials assembled in the structure process are inserted into the degreasing solution to remove any dirt or oil substances attached to the surface.
- Hydrochloric Acid Tank
- After degreasing, the steel materials are inserted into hydrochloric acid, and the mill scale (oxide layer) on the surface is removed. Alloy reactions do not occur between coated areas and zinc and become non-plated, so they are soaked in hydrochloric acid until they are completely removed to expose the iron base.
- Flux Tank
- After using hydrochloric acid, the steel materials are inserted into a flux tank to cover the surface with a coating to prevent the surface from rusting in the time that it is galvanized. In addition, by soaking the steel materials in flux, it promotes the alloy reaction between iron.


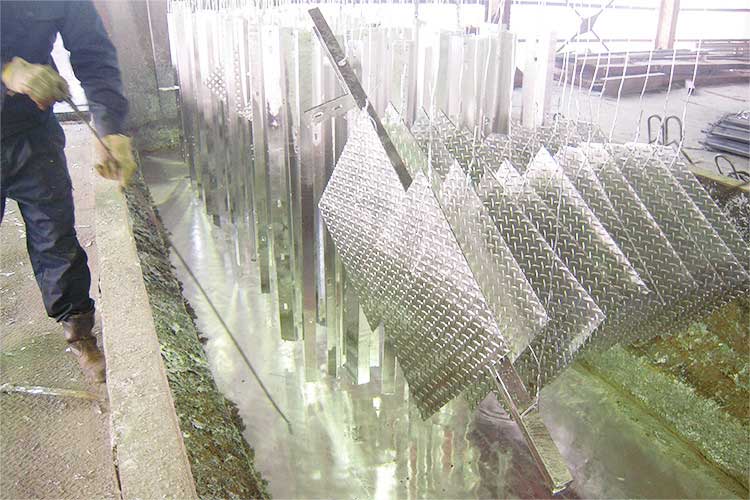
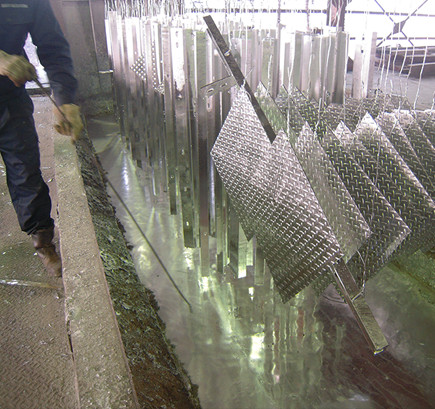
Galvanizing Process
- Plating Tank
- The steel materials processed with the flux substances are inserted into a melted plating tank that has a temperature of approximately 440℃. An alloy layer is formed between the surface of the steel materials and the zinc, creating a strong resistance to rusting.
- Cooling Water Tank
- The heated galvanized steel materials are then cooled in water. The bendable-shaped steel materials are cooled once before entering the cooling water tank.
- White Rust Prevention Tank
- Finally, the steel materials are inserted into a white rust prevention tank to form a coating layer on its surface to temporarily prevent white rust.

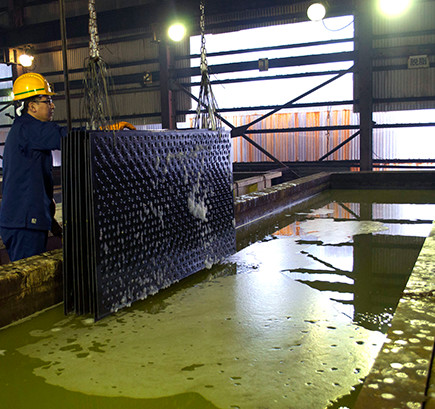
Finishing
The outer appearance of the steel material is checked, and the non-plated and unsharpened parts are given finishing touches using tools to repair any necessary parts.

Film Thickness Inspection
& Visual Inspection
In addition to conducting a visual inspection on the finished items, a special tool is used to inspect whether the galvanized plating amount exceeds the standard value.
Measurement
In addition to the visual and number checks of the finished goods, they are also carefully measured with a truck scale.


Structure Process
In order to advance the steel materials to the pretreatment process, they are assembled into optimal shapes depending on the required shape, number of units, and standards using various types of jigs.


Pretreatment Process
- Degreasing Tank
- The steel materials assembled in the structure process are inserted into the degreasing solution to remove any dirt or oil substances attached to the surface.
- Hydrochloric Acid Tank
- After degreasing, the steel materials are inserted into hydrochloric acid, and the mill scale (oxide layer) on the surface is removed. Alloy reactions do not occur between coated areas and zinc and become non-plated, so they are soaked in hydrochloric acid until they are completely removed to expose the iron base.
- Flux Tank
- After using hydrochloric acid, the steel materials are inserted into a flux tank to cover the surface with a coating to prevent the surface from rusting in the time that it is galvanized. In addition, by soaking the steel materials in flux, it promotes the alloy reaction between iron.


Galvanizing Process
- Plating Tank
- The steel materials processed with the flux substances are inserted into a melted plating tank that has a temperature of approximately 440℃. An alloy layer is formed between the surface of the steel materials and the zinc, creating a strong resistance to rusting.
- Cooling Water Tank
- The heated galvanized steel materials are then cooled in water. The bendable-shaped steel materials are cooled once before entering the cooling water tank.
- White Rust Prevention Tank
- Finally, the steel materials are inserted into a white rust prevention tank to form a coating layer on its surface to temporarily prevent white rust.

Finishing
The outer appearance of the steel material is checked, and the non-plated and unsharpened parts are given finishing touches using tools to repair any necessary parts.

Film
Thickness Inspection
& Visual Inspection
In addition to conducting a visual inspection on the finished items, a special tool is used to inspect whether the galvanized plating amount exceeds the standard value.
Measurement
In addition to the visual and number checks of the finished goods, they are also carefully measured with a truck scale.

Reason for Quick Delivery
Although it depends on the product, the entire process usually takes a total of half a day.
In addition to the 24-hour operation inside the factory, the introduction of an iPad in 2012 for production management has enabled us to confirm where our products are in real-time, and has significantly increased our work efficiency. In the future, in addition to our production management, we aim to continue creating a “viewable” distribution system that will enable our customers to confirm the status of the products.
Galvanizing Kettle Size
With our galvanizing kettle, it is possible to galvanize large products of up to 11 meters. The image below provides details of the galvanizing kettle.




